
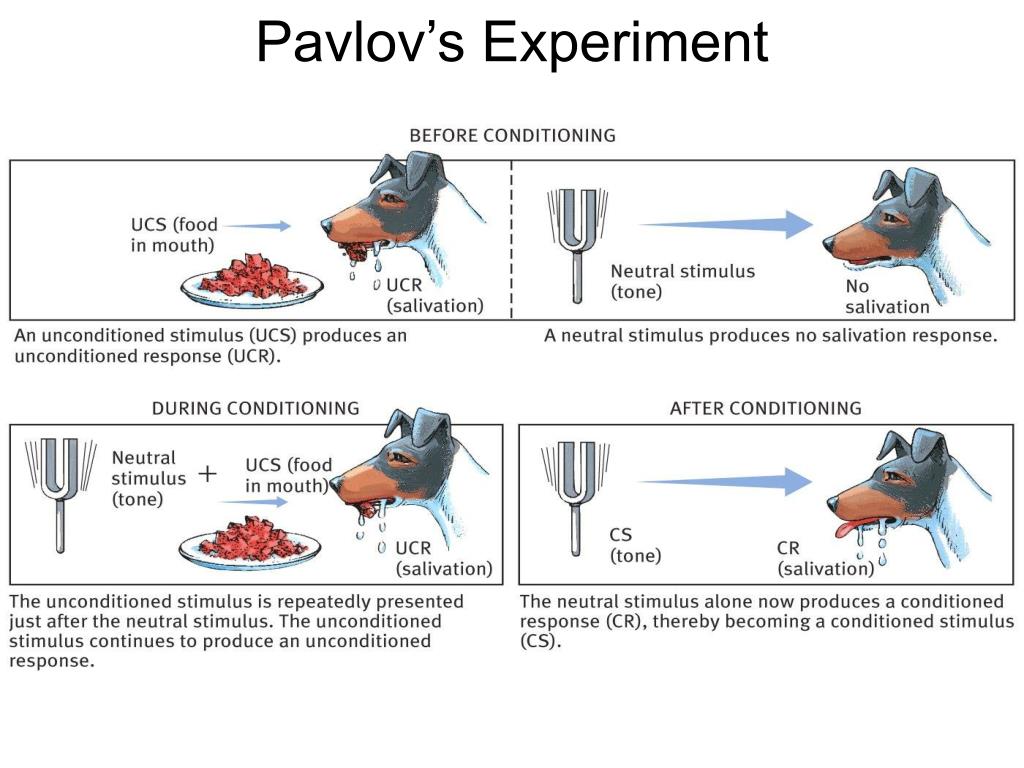
It attempted to replace depth psychology (Vladislav & Didier, 2018), considered having roots in the theories of Sigmund Freud, Carl Gustav, and Alfred Adler (Lewis, 1958). This looked at consequences that strengthen and weaken behavior. Behaviorism views the environment as the primary influence upon human behavior, not genetic factors (Thorndike, 1905).īehaviorism derived from the earlier research of Edward Thorndike (1905) and the Law of Effect in the later 19th century. Watson, like Pavlov, investigated conditioned neutral stimuli eliciting reflexes in respondent conditioning (Watson & Rayner, 1920). Behaviorism measures observable behaviors and events (Watson, 1913 Watson 1924). The following diagram (Figure 1) shows the different stages in the classical conditioning process in Pavlov’s (1897) dog experiments.Ĭlassical conditioning has its roots in behaviorism. They associated the bell with the arrival of food. After that, the sound of the bell on its own caused the dogs to salivate. Then when the food came out, the dogs realized the sound of the bell meant food, and they salivated. Pavlov rang a bell each time, just before feeding the dogs.
PAVLOV PSYCHOLOGY SERIES
Pavlov decided to undertake a series of experiments with the dogs to investigate these observations. This made Pavlov wonder why the dogs salivated when there was no food in sight. Sometimes this was just from the sight of the lab coats of the technicians feeding them. One interesting observation Pavlov made was that just before being given food, the dogs began to salivate.

The CR is a response that is made to the CS alone and without the UCS being required.Īs a physiologist, Ivan Pavlov (1897) researched digestion in dogs toward the end of the 19th century.

Learning is the process by which new knowledge, ideas, behaviors, and attitudes are acquired (Rehman, Mahabadi, Sanvictores, & Rehman, 2020). To understand classical conditioning theory, you first need to understand learning.

Classical Conditioning in Psychology History.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
